
BNC , short for Bayonet Neill–Concelman, utilizes an analog signal to connect via a coaxial cable. Commonly seen in surveillance & security systems. Advantages include a quick twist and lock mechanism for easy installation. HD-SDI (Hi-Definition Serial Digital Interface) looks nearly identical to the BNC, commonly used to deliver broadcast grade signal, capable up to 1.485 Gbit/s.
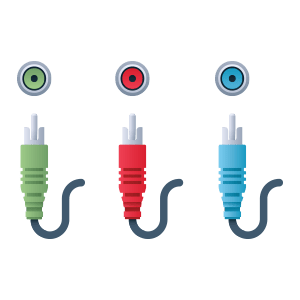
Component Video is used to deliver HD signal via two or more channels (most commonly done with 3 RCA type cables.) PAL, NTSC and SECAM are supported. Can carry high definition signal of 480p, 720p, 1080i, 1080p and higher. Commonly replaced with HDMI technology.

The new royalty-free high definition standard by VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) that is able to transmit 4K at a bandwidth of 32.4 Gbit/s. DisplayPort 1.4 adds Display Stream Compression (DSC), Forward Correction and the latest HDR10 technology. The new DSC technology is nearly lossless and supports 8K over 60Hz or 4K over 120Hz.
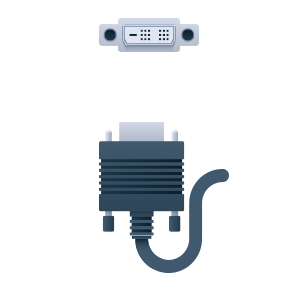
DVI stands for “Digital Visual Interface” – The D means “digital” which means that it will only transmit digital signal. This interface is less common as DVI-I since it is more universal. DVI has a maximum bandwidth of 4.95 Gbit/s for single link and 7.92 Gbit/s. for dual link. Up to 3840×2400 resolution at 17 Hz (single link) and 3840×2400 resolution at 33 Hz via dual link. This makes this technology ideal for 1080P or lower.
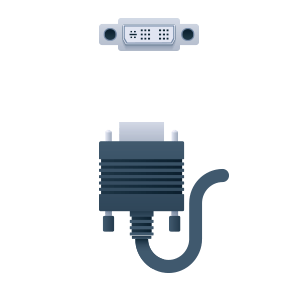
DVI-I is a more common interface that is capable of transmitting both analog and digital signals. The “I” stands for “integrated”. It is identical to the DVI-D interface above except it features 27-pin vs 24-pin design (DVI-D) in order to be backward compatible with analog signals (common when using a VGA adapter).

HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is used to deliver uncompressed full HD signals. Current revision 2.0b is backward compatible with resolutions of up to 4K at 60 Hz and 32 audio channels all from a single cable. Version 2.0b also supports HDR and simultaneous delivery of dual streams for multiple users. The most common interface to deliver HD and 4K signal in 2016 & 2017.

RCA (Radio Corporation of America) is a standard definition cable introduced in the early 1940s. It became popular in the 1950s and was able to deliver video on one coaxial cable and stereo audio via two cables (one cable for left and one for right). This cable is not callable of high definition video transfer until it has been upgraded to the composite version as shown above.

S-Video (also known as separate video or Y/C), which is a standard in standard definition video. Common resolutions include 480i and 576i which is also believed to have better picture quality than standard RCA capable. 4, 7 or 9 pin are common and designed to work with NTSC, PAL and SECAM video systems.
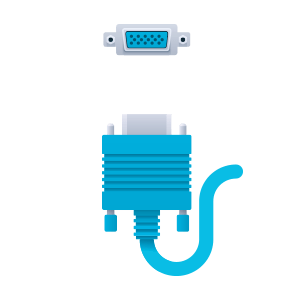
VGA (Video Graphics Array) First introduced in 1987 and still is a standard in computer monitors which uses a standard analog signal capable from standard VGA resolutions (640×480) through QXGA (2048×1536px) @ 85 Hz. This technology is now slowly phasing out in favor of HDMI and DisplayPort technologies.
Have a question about input cables? Talk to a display expert today 888-623-2004 ext 231 or use our live website chat support (available Monday – Friday 9am – 5pm CST).